Design thinking is by no means a new practice. But what is design thinking in HR, and how can departments employ it to work better?
Here is a quick explanatory guide on how design thinking should be used as an axis to evolve HR functions.
What is Design Thinking?
Design thinking describes the perceptive reasoning used to create strategies and processes that surround concept designs and developments.
Getting started with Design Thinking
There are five stages in design thinking:
- Emphatize
Observe carefully and freely. Judgment and set ideas have to go out the window. Observing with complete empathy can help reveal issues that users may not even know they have. It means you can solve a problem before it affects a customer and, ultimately, your business.
- Define
It is where the data you’ve collated from your observation gets whittled down to a core issue. Once the periphery gets removed, you are left with a clear definition of the problem. Therefore, you are one step closer to a solution.
- Ideate
It is a part of traditional problem-solving that comes in at a much later stage. The team sits down after analyzing the data and comes up with as many different ideas as possible that could lead towards a solution.
- Prototype
It is where these ideas are poised to become solutions. This stage is where the solutions are formed and ready to be executed.
- Test
As the name suggests, this is where you test the solution to see if it works. It should change the interaction of the end-users on some level. Then, you collect feedback from them and determine if they like the changes and positively impact them.
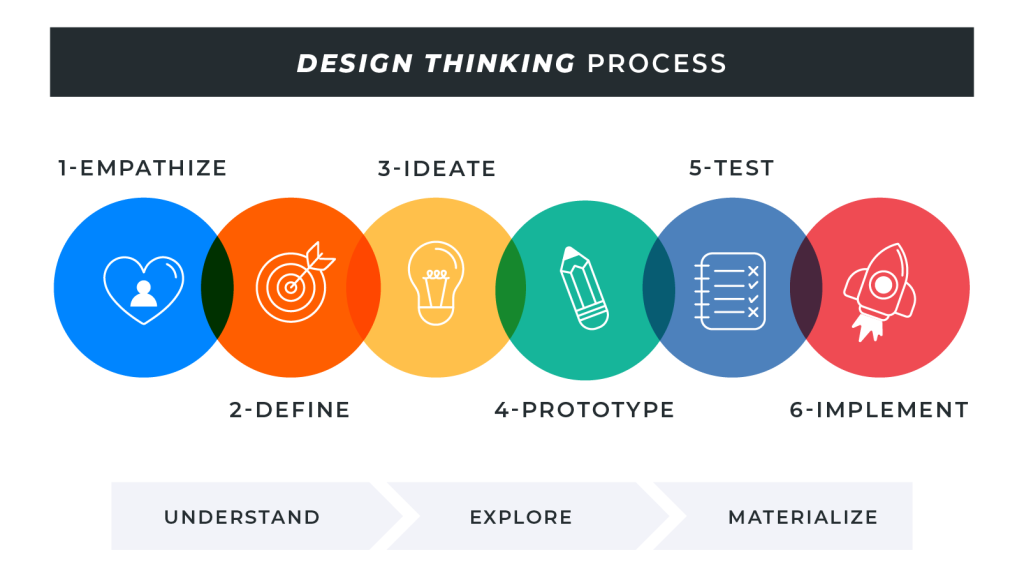
Of course, after doing this, you go back to the drawing board and start the process all over again.
Here are some key points to remember:
- Have the right focus
Be sure of what your focus is. Make sure that the issue that you are attempting to solve is the one you need to solve.
- Be ready to move
A crucial part of design thinking in HR is adapting to the input. Let the process of learning be the factor that you use to determine the next step. Staying agile when receiving feedback from your end-users allows the plan to be more effective.
- Empathy, Empathy, Empathy
Step into the role. To understand the problem you are trying to solve, step into the role of the end-user. Watch what the users do, how they do it, and how they interact with their surroundings and understand why they react the way they do.
What is Design Thinking in HR
At its core, design thinking in HR is a process that prioritizes the customers’ needs and then creates solutions around that problem.
The learnings are based on empathetic observations of how people behave in specific environments and react to the happenings in that environment. Thus, the approach is a hands-on method of creating innovative solutions. The human element of thinking is at the center of the design.
To reiterate, design thinking creates processes around humans, and not simply for humans. Therefore, it relies on evidence of how humans behave towards a product or service and continuously improves that experience.
The method we all know and use to solve problems is to identify the concern, then investigate and find solutions. Design thinking doesn’t focus on creating one solution. Instead, it is a continuous process of adapting thought and approach to meet the end-user needs.
How to implement Design Thinking in HR?
The question again, how can design thinking in HR help it function:
1. Recruitment and Onboarding
Design thinking principles can be integrated into the hiring and recruiting function of HR. A simple example of design thinking in HR is creating a comfortable atmosphere in interviews and new employees on the floor is a great way to get the best out of them. A nervous interviewee isn’t going to be able to show you what they are capable of.
By understanding or empathizing with them you shatter the barriers that are holding them back from being all they can be. Empathy also allows human resource personnel to weed out any processes or tactics that aren’t ideal for their recruitment strategy because you are made to think like a new hire or an interviewee.
During recruitment, you have the opportunity to collect unbiased raw feedback about the hiring process and even the company’s image. It makes the ideation part of design thinking easier too. You get your ideas directly from the new hires or candidates.
Savvy HR executives should also be able to test these learnings immediately and garner feedback from them. It helps improve the process continually. Of course, the same thought can get applied during the onboarding process as well.
2. Employee Performance
This can be a complex area to analyze or get accurate data from graphs and charts. However, by applying design thinking within HR processes, a continuous feedback loop allows employees to share their grievances and let the HR department know how they prefer to be rewarded for performance.
Surveys and meetings with employees on a one-on-one level can garner accurate feedback and understand what they expect. It also gives HR departments the ability to create performance incentives that employees prefer, thereby driving their performance.
When employees realize that their feedback has been incorporated, they have more reason to align their efforts towards the HR strategy and the business goals.
3. Managing Relationships
An essential function of HR management is to ensure that employers and employees communicate their needs and wants effectively. Implementing the empathy aspect of design thinking in HR functions like these allows for open lines of communication.
Using design thinking principles, HR departments can quickly assess and resolve issues and barriers in communication.
4. Payroll and Benefits
It is a massive chunk of what HR is responsible for. Design thinking helps HR departments understand what benefits and incentives are required to ensure a happy employee who works effectively and productively. Creating design thinking policies is an intelligent way to meet employee needs while remaining true to business goals.





