Introduction
In today’s data-driven business world, organizations are increasingly turning to Human Resources (HR) Analytics to make smarter, evidence-based workforce decisions. Also known as people analytics or workforce analytics, this approach uses data analysis, statistical modeling, and machine learning to uncover insights about employee behavior, performance, and organizational efficiency.
By applying HR analytics, companies can transform raw workforce data into actionable insights that improve hiring, engagement, retention, and productivity ultimately driving better business outcomes.
Defining Human Resources Analytics
Human Resources Analytics is the systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting workforce data to inform HR strategies and decision-making. It involves gathering data from multiple sources—such as employee surveys, performance reviews, attendance records, and payroll systems and applying statistical tools to identify trends, patterns, and relationships.
The ultimate goal of HR analytics is to enable data-driven HR management. Organizations use it to:
- Identify areas where performance or engagement can be improved
- Forecast future workforce needs
- Design targeted talent management and retention strategies
- Optimize recruitment and training investments
By leveraging analytics, HR professionals move from intuition-based decisions to strategic, evidence-based insights that enhance organizational effectiveness.
The Four Main Types of HR Analytics
HR analytics can be categorized into four major types—each serving a unique purpose in understanding and improving workforce performance.
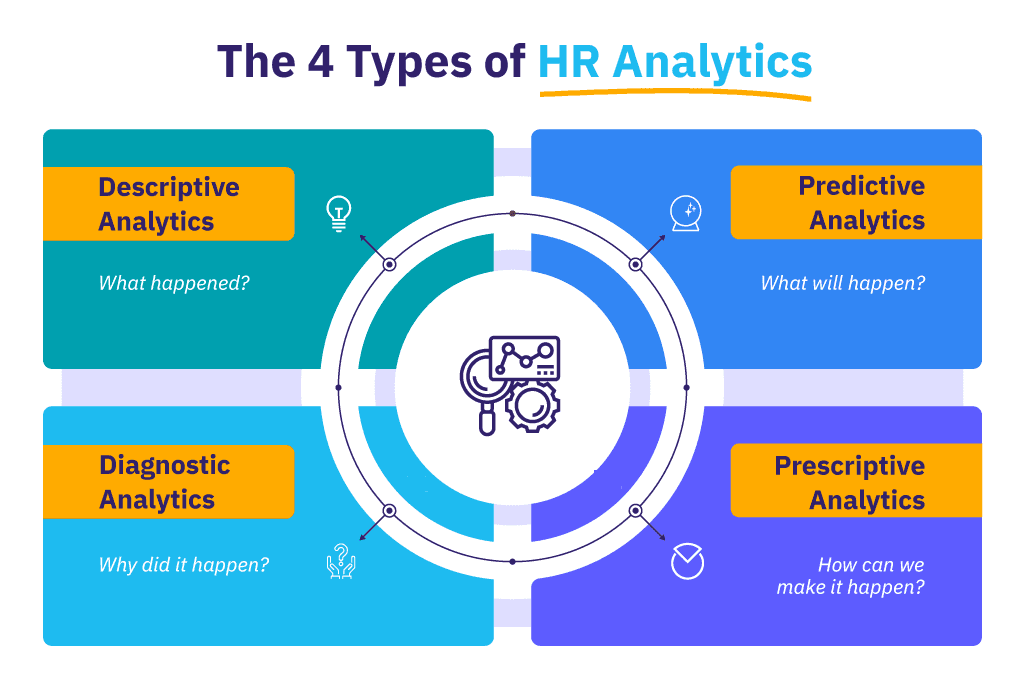
1. Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics focuses on understanding what has already happened in the organization.
It summarizes historical data to reveal trends, relationships, and outcomes.
For example, HR professionals can use descriptive analytics to answer questions like:
- “How many employees were hired or promoted in the last quarter?”
- “What is the turnover rate for the marketing department?”
This foundational level of analytics provides a snapshot of workforce dynamics and sets the stage for deeper analysis.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics goes a step further by exploring why something happened.
It identifies the root causes of workforce issues, helping HR leaders understand the underlying drivers behind trends revealed through descriptive analytics.
Example questions include:
- “Why is the turnover rate higher in one department than others?”
- “Why are certain employees consistently underperforming?”
This type of analysis helps HR teams design targeted interventions to address issues at their source.
3. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses statistical models, historical data, and machine learning to forecast future HR outcomes. It enables organizations to anticipate challenges and prepare proactive solutions.
For instance, predictive analytics can answer questions like:
- “What is the likelihood that top-performing employees will leave within six months?”
- “How many new hires will we need next year to meet growth targets?”
By forecasting trends, predictive analytics empowers HR teams to plan for the future and reduce uncertainty in workforce management.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics takes HR insights to the next level by recommending specific actions or strategies to achieve desired outcomes.
It not only identifies what might happen but also suggests what should be done about it.
Example applications include:
- Determining which training programs can boost productivity
- Identifying which engagement initiatives can reduce turnover
- Recommending optimal recruitment strategies to attract high-quality candidates
Prescriptive analytics helps HR leaders make informed, strategic decisions that directly improve employee satisfaction and business performance.
Why HR Analytics Matters
Implementing HR analytics helps organizations move beyond guesswork and embrace evidence-based management. Some key benefits include:
- Improved decision-making: Data-backed insights reduce bias and enhance objectivity.
- Enhanced employee engagement: Analytics can reveal what truly motivates employees.
- Reduced turnover: Predictive insights help identify and retain at-risk employees.
- Increased profitability: Efficient workforce planning leads to better business outcomes.
By understanding their workforce through data, organizations can create smarter strategies for recruitment, development, and retention turning HR into a true strategic partner in business success.
Conclusion
Human Resources Analytics is revolutionizing how organizations manage people. By combining data science with human insight, HR professionals can make better decisions, anticipate workforce challenges, and design strategies that enhance performance and engagement.
Whether through descriptive reporting or advanced predictive modeling, HR analytics empowers businesses to turn data into action driving both employee satisfaction and long-term organizational growth.








