Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) focuses on designing and implementing HR strategies that align the efforts, skills, and behavior of employees with the long-term objectives of the organization. In essence, it ensures that every human resource activity contributes directly to achieving business goals and maintaining a competitive edge.
Strategic Human Resource Management Process
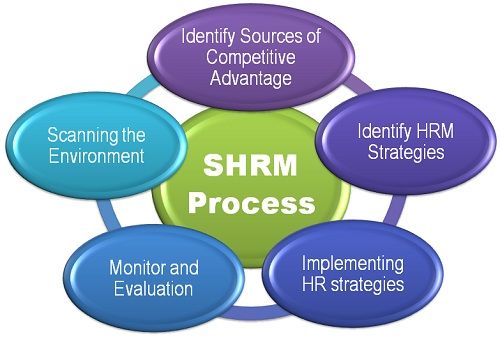
1. Scanning the Environment
The SHRM process begins with a comprehensive environmental scan, which involves examining both external and internal factors that influence the organization’s performance.
- External Environment: Includes political, legal, technological, economic, social, and cultural factors that shape the overall business landscape. These elements can create opportunities or threats for the organization.
- Internal Environment: Encompasses aspects such as organizational structure, culture, business processes, industrial relations, and results from SWOT analyses (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats). These internal components determine how efficiently a business operates and adapts to change.
The HR department plays a vital role in gathering intelligence about competitors—such as their strategies, mission, vision, strengths, and weaknesses. Insights can be collected from various sources, including resumes submitted by candidates from rival firms. This information helps HR professionals understand competitor work cultures, compensation standards, employee skills, and turnover reasons, ultimately guiding better workforce strategies.
2. Identify Sources of Competitive Advantage
Once the environment is assessed, the next step is to identify areas of competitive advantage. These can arise from multiple business dimensions such as:
- Product quality
- Pricing strategy
- Customer service
- Brand reputation
- Distribution and delivery efficiency
HR departments contribute to achieving competitive advantage by investing in training and development programs that enhance employee skills, improve efficiency, and foster innovation. Well-trained employees are better equipped to deliver superior value to customers and drive organizational success.
3. Identify HRM Strategies
At this stage, organizations design specific HR strategies that align employee capabilities with organizational goals. Typically, four strategic approaches are adopted:
a) Learning as Socialization
This approach uses training sessions, coaching, and education programs to ensure employees understand and embody the organization’s core values, beliefs, and goals. It helps align personal performance with business expectations.
b) Devolved Informal Learning
This strategy encourages employees to explore and take advantage of informal learning and career development opportunities. It fosters continuous growth and a proactive learning culture within the organization.
c) Engineering
Here, the focus is on building and nurturing communities of practice and social networks—both internal and external. These communities enhance knowledge sharing, collaboration, and innovation.
d) Empowered Informal Learning
This strategy creates an environment that promotes learning through practice—such as exposure to new processes, restructured workspaces, and shared knowledge hubs. The HR department ensures that employees are continuously learning and adapting to change.
4. Implementing HR Strategies
After selecting the most suitable HR strategies, the next critical phase is implementation.
This involves translating strategic plans into practical actions through:
- HR policies
- Workforce planning
- Recruitment and selection processes
- Training and development initiatives
- Performance management systems
Effective implementation ensures that all HR activities support the organization’s strategic objectives.
5. Monitor and Evaluation
The final phase of the SHRM process is monitoring and evaluation.
At this stage, HR professionals assess whether the implemented strategies are achieving the desired results. This involves:
- Setting clear performance targets and tolerance levels
- Measuring actual outcomes against established benchmarks
- Identifying deviations and areas of improvement
- Making necessary adjustments or redesigning strategies
Continuous evaluation ensures that HR strategies remain relevant, effective, and adaptable to changing business needs.
Conclusion
A well-structured Strategic Human Resource Management Process helps organizations build a strong, skilled, and motivated workforce that drives business performance. By systematically scanning the environment, identifying competitive strengths, developing targeted HR strategies, and continuously evaluating their effectiveness, companies can ensure that their HR functions contribute directly to long-term organizational success.








