The Human Resource Management model contains all Human Resource activities. When these activities are discharged effectively, they will result in a competent and willing workforce who will help realize organizational goals. There is another variable in the model – environment. It may be stated that the Human Resource function does not operate in vacuum. It is influenced by several internal and external forces like economic, technological, political, legal, organizational, and professional conditions.
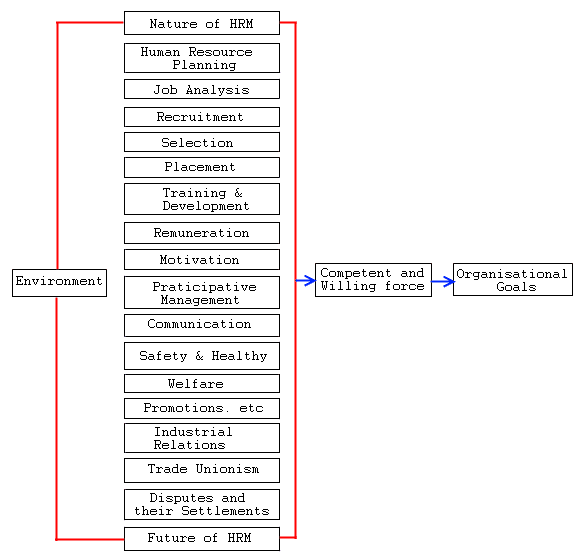
Human Resource Management: is a management function that helps the managers to recruit, select, train, and develop members for an organization.
Human Resource Planning: Human Resource Planning is understood as the process of forecasting an organizations future demand for, and supply of, the right type of people in the right number.
Job Analysis: Job analysis is the process of studying and collecting information relating to the operations and responsibilities of a specific job. The immediate products of this analysis are job descriptions and job specification.
Recruitment: Recruitment is the process of finding and attracting capable applicants for employment. The process begins when new recruits are sought and ends when their applications are submitted. The result is a pool of applicants from which new employees are selected.
Selection: is the process of differentiating between applicants in order to identify (and hire) those with greater likelihood of success in a job.
Placement: is understood as the allocation of people to jobs. It is the assignment or reassignment of an employee to a new or different job.
Training and development: it is an attempt to improve current or future employee performance by increasing an employee’s ability to perform through learning, usually by changing the employee’s attitude or increasing his or her skills and knowledge. The need for training and development is determined by employee’s performance deficiency, computed as follows: Training and development need = Standard performance – Actual performance
Remuneration: is the compensation an employee receives in return for his or her contribution to the organization.
Motivation: is a process that starts with a psychological or physiological deficiency or need that activates behavior or a drive that is aimed at a goal or an incentive.
Participative management: Workers participation may broadly be taken to cover all terms of association of workers and their representatives with the decision making process, ranging from exchange of information, consultations, decisions and negotiations to more institutionalized forms such as the presence of workers members on management or supervisory boards or even management by workers themselves as practiced in Yugoslavia. (ILO)
Communication: may be understood as the process of exchanging information, and understanding among people.
Safety and health: Safety means freedom from the occurrence or risk of injury or loss. In order to ensure the continuing good health of their employees, the HRM focuses on the need for healthy workers and health services.
Welfare: as defined by ILO at its Asian Regional Conference, defined labour welfare as a term which is understood to include such services, facilities, and amenities as may be established in or in the vicinity of undertakings to enable the person employed in them to perform their work in healthy, congenial surroundings and to provide them with amenities conducive to good health and high morale.
Promotions: means an improvement in pay, prestige, position and responsibilities of an employee within his or her organization.
Transfer: Transfer involves a change in the job (accompanied by a change in the place of the job) of an employee without a change in the responsibilities or remuneration. Separations: Lay-offs, resignations and dismissals separate employees from the employers.
Industrial relations: Industrial relations is concerned with the systems, rules and procedures used by unions and employers to determine the reward for effort and other conditions of employment, to protect the interests of the employed and their employers, and to regulate the ways in which employers treat their employees.
Trade Unions: Trade unions are are voluntary organizations of workers or employers formed to promote and protect their interests through collective action.
Disputes and their settlement: Industrial disputes mean any dispute or difference between employers and employers, or between employers and workmen, or between workmen and workmen, which is connected with the employment or non-employment or terms of employment or with the conditions of labour of any person.







